Evolution of Dissolution Testing
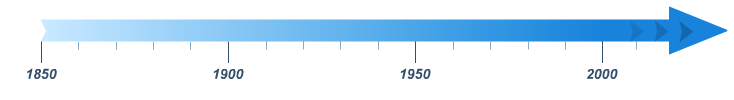
Timeline
The above timeline shows the period from 1850 to present day. Each of the three 50 year time periods and the time period 2000 onwards can be selected with your cursor to view more information about that particular era of dissolution history. Significant years are indicated with blue flags. Click on the flags to view more information.
1900 Brunner and Tolloczko
Brunner and Tolloczko prove the dissolution rate depends on the chemical and physical structures of the solid, the surface area exposed to the medium, agitation speed, medium temperature and the overall design of the dissolution apparatus.
1897 Noyes and Whitney
Noyes and Whitney publish a paper of 'The Rate of Solution of Solid Substances in Their Own Solution' suggesting dissolution rate is controlled by a layer of saturated solution that forms instantly around a solid particle.
1904 Nernst and Brunner
Nernst and Brunner use laws of diffusion to introduce a new relationship between the dissolution rate constant and the diffusion coefficient of the solute.
1930 Experiments
Experiments begin with in vitro/in vivo correlation and bioavailability.
1931 Hixson and Crowell
Hixson and Crowell develop a mathematical model describing the dissolution process.
1932 Solvometer
The Solvometer is introduced. Chemical substances were compressed into a tablet of uniform surface area to study surface rate dissolution … the forerunner of modern intrinsic studies.
1934 Disintegration Test
Pharmacopoeia Helvetica in Bern, Switzerland is the first regulatory body to incorporate a disintegration test for tablets.
1950 Official Approval of Disintegration Test
The disintegration test becomes an official USP method. (USP XIV).
1955 Solid Dosage Form Test
USP XV requires the disintegration test for most solid dosage forms.
1958 Rotating Bottle Method
The rotating bottle method is developed to study timed-release formulations.
1960 Levy and Hayes
Levy and Hayes, utilizing a beaker and three-blade stirrer at 30-60 RPM, find significant differences in the in vitro dissolution rate of different brands of aspirin tablets and link them to the incidence of gastrointestinal irritation caused by various brands of aspirin tablets due to their slow dissolution rates.
1960 and Later
- It becomes apparent that disintegration has little to do with biological activity. Disintegration was important, but deaggregation was essential for bioavailability.
- USP-NF Joint Panel recognizes a need for a dissolution test.
- William Mader and Dr. Lee T. Gradey with the Drug Standards Laboratory, experiment with a variety of basket and stirring devices.
- USP-NF Joint Panels adopt the rotating basket apparatus to test individual dosage units.
1962 Amendments Passed
Kefauver-Harris Drug Effectiveness and Safety Amendments are passed.
1967 Regulations
USP-NF Panel on Physiological Availability establish regulations to assure drug effectiveness.
1969 Flow Through Cell
The circulating Flow Through Cell is developed.
1970 Rotating Basket
- USP XVII incorporates the first official dissolution test for solid dosage forms
- Twelve monographs are published in USP-NF with the official dissolution test - rotating basket
Early 1970s
- Scientists evaluate variability seen in dissolution results from one apparatus to another.
- NCDA (FDA) finds variability between apparatus-to-apparatus and lab-to-lab.
- FDA and USP push for standardization of dissolution testing.
1975 Calibrators
- The USP Revision Subcommittee on General Chapters begins development of calibrators for dissolution testing.
- The USP Subcommittee recommends two apparatus - the Rotating Paddle and Rotating Basket.
1977 Bioequivalence Testing
FDA publishes the need for bioequivalence testing.
1978 Further Study
- FDA publishes Guidelines for Dissolution Testing.
- USP publishes Pharmaceutical Manufactures Association (PMA) Collaborative Study result for three colibrators - Prednisone, Salicylic Acid and Nitrofuration.
- USP proposes conditions 50, 100, and 150 RPM for baskets; 50 and 100 RPM for paddles; time points: 15, 30, 45, and 60 minutes (40 tests).
- PMA suggests averaging and standard deviation as acceptance criteria.
- FDA - USP finds individual tablet criteria unacceptable. Averages are too wide.
- USP issues first official refrence standard calibrator tablets.
- All dissolution equipment used for compendial dissolution testing must meet USP calibrator acceptance criteria.
1984
FDA/DPA publishes the 'Guidelines for Dissolution Testing Addendum'.
1996 An Alternative Approach to PVT
- A Subcommitte on dissolution Calibration is formed within the dissolution Subcommitte of the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers (PhRMA) in 1996.
- A collaborative on pertubation is performed by twelve PhRMA laboratories; the goals are to:
- Evaluate alternative dissolution apparatus suitablity test requirements
- Identify which aspects of colibration add value to the evalution of bath performance
- Evaluate non-value added activities performed during dissolution calibration,
including the potential elimination of calibrator tablets
1997 Pooled Sampling, USP Calibration Requirements, FDA Guidance
Pooled Sampling
- Pooled sampling is added to USP XXIII seventh Suplement. It is later removed.
- Food And Drug Administration Modernization Act reauthorizes Prescription Drug User Free Act of 1992 and mandates the most wide-ranging reforms in agency practices since 1938. Provisions include measures to accelerate review of devices, regulate advertising of unapproved uses of approved drugs and devices, and regulate health claims for foods.
USP Calibration Requirements
- USP Calibration requirements are reduced to 4 tests total:
- Disintegrating and non-disintegrating tablets
- 50 and 100 RPM - one speed each apparatus
- Each test had individual acceptance ranges (4 total)
- Apparatus dedicated for paddle for basket require only two tests
FDA Guidance for industry Documents Introduced
- 'Dissolution Testing of Immediate Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms' (August)
- 'Extended Release Oral Dosage Forms: Development, Evaluation, and Application of In Vitro/In Vivo Correlations' (September)
- 'Scale-Up and Postapproval Changes for Modified Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms "SUPAC-MR" ' (September)
2000 Guidance for Industry, An Alternative Approach to PVT
Guidance for Industry
FDA Guidance for Industry 'Waiver of In Vivo Bioavailability and Bioequivalence Studies for Immediate-Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms Based on a Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS)'.
2003 FIP/AAPS Guidelines - Novel/Special Dosage Forms
FIP/AAPS Guidelines to Dissolution In Vitro Release Testing of Novel/Special Dosage Forms.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2750303/pdf/12249_2008_Article_
41043.pdf
2007 Qualification of Apparatus, Toolkit Dissolution Procedure, Chapter <1092>
Qualification of Basket and Paddle Dissolution Apparatus
- Standard Practice for Qualification of Basket and Paddle Dissolution Apparatus
American Society for Testing and Materials, International (ASTM), Designation E 2503-07, Effective Date: 15 March 2007.
http://www.astm.org/Standards/E2503.htm- Cost: $32.00 USD
- E2503 is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E55 on Manufacture of Pharmaceutical Products and is the direct responsibility of Technical Subcommittee E55.03 on General Pharmaceutical Standards
Toolkit Dissolution Procedure
- Toolkit Dissolution Procedure: Mechanical Calibration and Performance Verification Test, United States Pharmacopeia (USP), Version 1.0, Draft 5.1,
4 October 2007. Version 2.0 available March 2010.
http://www.usp.org/sites/default/files/usp/document/our-work/reference-standards/dissolution-toolkit-version2.pdf- Free Download
- Provides very detailed mechanical calibration procedure along with measuring techniques, tools required, and frequency of measurement
- Requires the use of the USP Performance Verification Test (PVT)
USP Added General Chapter <1092>
- USP added General Chapter <1092> The Dissolution Procedure: Development and Validation.
2011 FDA Guidance for Industry
FDA Guidance for Industry: Q4B Evaluation and Recommendation of Pharmaceutical Texts for Use in ICH Regions, Annex 7(R2) Dissolution Test General Chapter:
http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatory
Information/Guidances/ucm085366.pdf

